Sustainable Solutions for Septic Systems: A Modern Approach to Waste Management
Key Takeaways
- Discover innovative strategies for managing household waste sustainably with advanced septic systems.
- Explore diverse designs and technologies, enhancing environmental quality and system efficiency.
- Gain insights on regulatory guidelines and user-friendly practices for effective septic system maintenance.
Introduction
As environmental consciousness grows, the imperative for sustainable solutions in waste management becomes clearer. Septic systems, pivotal in efficiently processing household sewage, are embracing advanced technologies to reduce their environmental impact. One groundbreaking advancement in this domain is the nitrogen-reducing septic system. This system exemplifies a forward-thinking approach, seamlessly integrating into homes to tackle sewage management sustainably.
Such systems employ comprehensive methods incorporating biological and chemical treatments designed to eliminate excess nitrogen, a primary source of waterway pollution. These enhancements promote a healthier ecosystem and correspond with the worldwide movement to reduce water and energy usage in all areas of life.
The resulting systems offer an enhanced capability to manage sewage effectively while maintaining ecological balance.
Waste Management Reimagined
The concept of waste management has transformed rudimentary disposal methods into a cohesive science addressing today’s environmental concerns. Contemporary septic systems, including commercial septic solutions, are key players in this development, providing sustainable and efficient waste treatment options. Redesigning household and commercial sewage management systems significantly lowers pollution, improves cleaner ecosystems, and promotes community health. The possible future advantages consist of considerably reduced pollution of groundwater supplies and a notable reduction in environmental harm linked to conventional waste management methods.
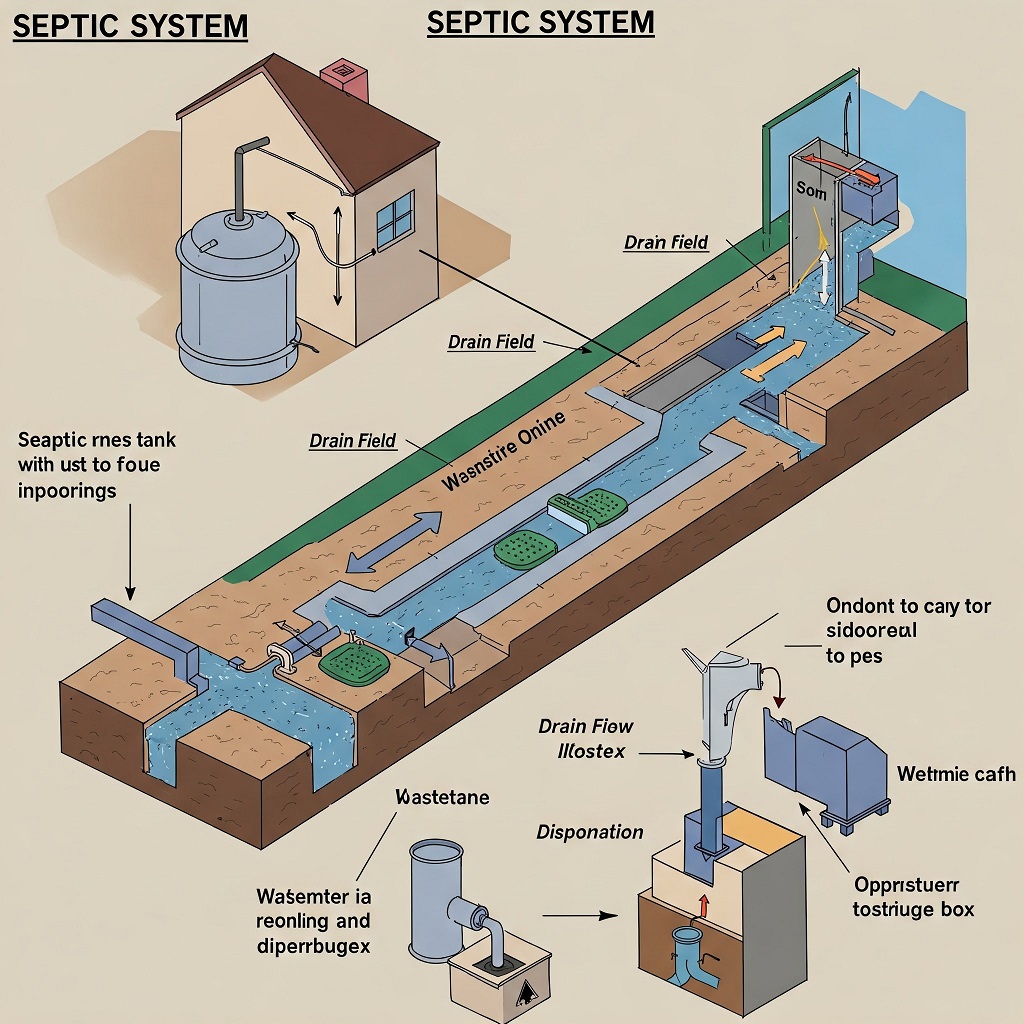
The Science Behind Modern Septic Systems
Modern septic systems use sophisticated technology to optimize waste treatment. These systems integrate a synergistic blend of physical, chemical, and biological processes. Physical components include filters that remove solids, while biological systems utilize beneficial bacteria to decompose organic matter. Chemical processes often involve treatments that neutralize pathogens. Together, these elements ensure that the waste output is as harmless and environmentally friendly as possible, a concept thoroughly covered by the EPA’s overview of septic systems.
Advantages of High-Efficiency Septic Designs
High-efficiency septic designs stand out because they can significantly mitigate the ecological impact of household waste. By substantially lowering nitrogen emissions, these systems protect water bodies from nutrient surpluses, which can result in harmful algal blooms and various ecological disruptions.
Furthermore, they require less frequent pumping and maintenance, reducing homeowners’ long-term costs. Adequate water and energy use also results in a significantly smaller carbon footprint for these systems than traditional options, making them a favored selection among environmentally aware homeowners.
Key Features of Advanced Systems
Today’s advanced septic systems boast a range of innovative features. Aerobic treatment units inject extra oxygen to speed up waste breakdown, while sand filters provide robust secondary treatment. Advanced disinfection processes, such as ultraviolet light treatments, further prevent lingering pathogens. These technologies collectively strive to produce cleaner and safer water, minimizing pollution risks and contributing positively to public health by preventing disease spread.
Environmental and Economic Impacts
Transitioning to sustainable septic systems offers environmental and financial benefits. From an ecological perspective, these systems help prevent pollution in water bodies, significantly reducing the risk of nutrient contamination and promoting biodiversity. Economically, sustainable septic systems invest in longer-lasting solutions that require less maintenance, leading to substantial savings over time. Additionally, reducing water and electricity usage saves individual households money and supports national energy conservation and resource sustainability initiatives.
Regulatory Considerations and Compliance
Regulatory frameworks governing septic systems ensure that installations adhere to stringent environmental and safety standards, safeguarding public health and environmental respect. Compliance with these regulations not only aids in maintaining system performance but also plays a pivotal role in driving innovation, reflecting society’s ever-increasing ecological expectations. Authorities enforce regular inspections and mandates that keep system owners accountable, ensuring ongoing operational excellence and eco-friendly performance.
Maintaining Your Septic System
Proper maintenance of septic systems is essential for their longevity and efficiency. Regular inspections can identify problems before they develop into costly repairs. Additionally, practicing sensible water usage and managing household chemicals that enter your plumbing can significantly extend the life of your septic system. Simple actions like these help minimize the need for frequent pumping and ensure that the system operates at its best. This not only supports a healthier environment but also saves homeowners money. For more comprehensive guidance on proper septic system care, the Environmental Protection Agency offers valuable tips and recommendations.
Future Perspectives on Waste Management
The future direction of septic systems is geared toward even more excellent responsiveness to environmental needs. Emerging technologies, including IoT devices for continuous monitoring and diagnostics, herald an era of more competent waste management. These advances promise not only increased operational efficiencies but also greater accessibility and ease of maintenance. Ultimately, they represent a commitment to sustainable living that supports a balance between meeting human needs and protecting the natural world.
